Fujikura FSM-100 Special Fiber Splicer Series
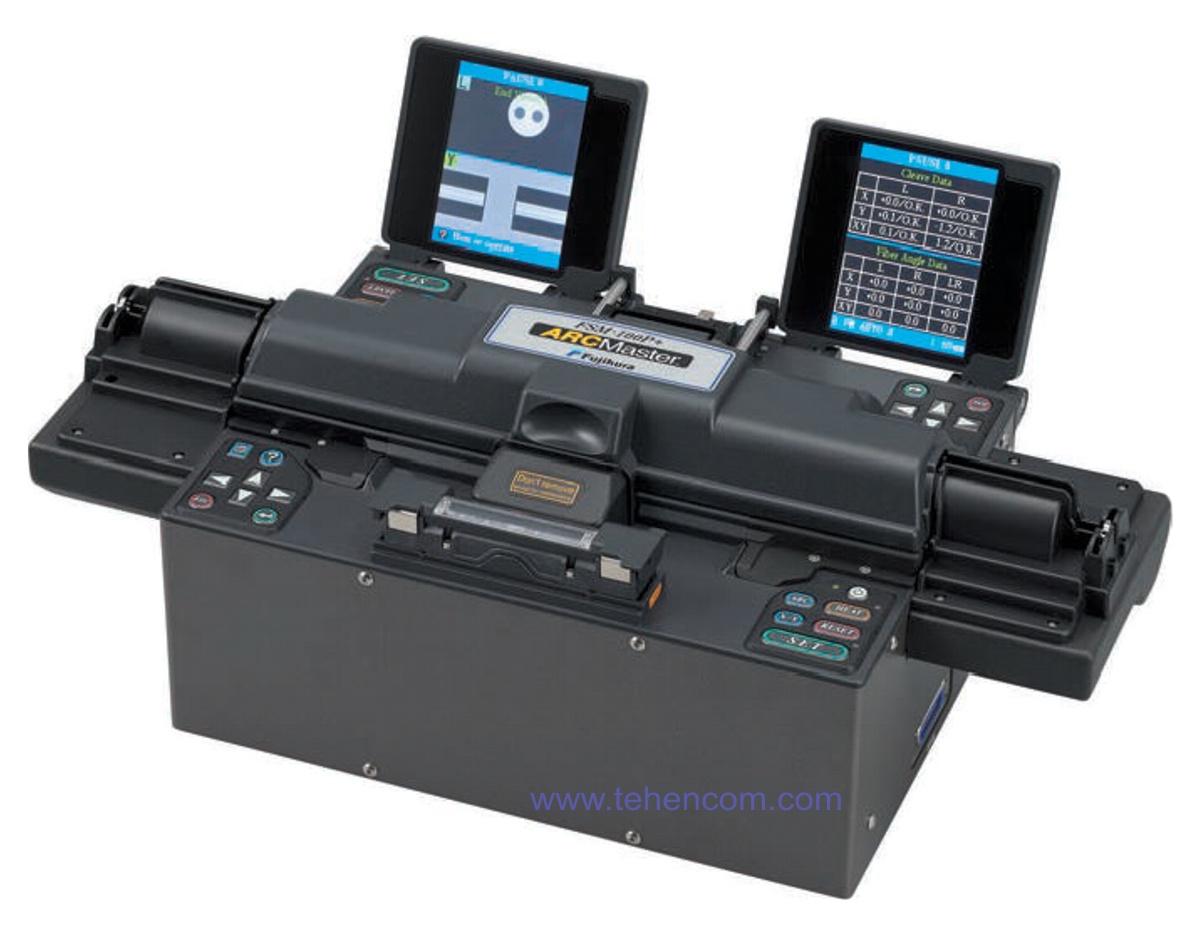

Product code: 1000239
Add item to cart. Our specialist will coordinate with you the complete set, tell you the price and delivery time.
Price on request
SHORT DESCRIPTION
Welding Machine Series Fujikura FSM-100 designed for splicing various types of special optical fibers: small and large diameter, polarization-preserving, non-round, with holes, and so on. The FSM-100 series consists of four models that differ in their set of functions: FSM-100M, FSM-100M+, FSM-100P and FSM-100P+.
The FSM-100M+ and FSM-100P+ models can splice the largest diameter fibers (up to 1200 µm) and have additional mirrors to analyze fiber ends before splicing. The FSM-100P and FSM-100P+ models can splice polarization-preserving fibers. In the FSM-100 series, the most functional model is the Fujikura FSM-100P+. You can download a full description of all the characteristics of Fujikura FSM-100 devices below on this page in the section Documentation.
Areas of use:
- laser installations;
- optical components;
- optical devices;
- sensory systems;
- medical equipment;
- Scientific research.
Main characteristics:
Precise alignment with optical fiber rotation (IPA technology).
Precise alignment to the optical fiber core (PAS technology).
Types of fibers to be welded: PMF, LDF, NZDS (G655), SM (G652), MM (G651), EDF, DCF, etc.
Average splice loss: 0.06dB (PMF), 0.05dB (LDF/NZDS), 0 .03 dB (SM), 0.02 dB (MM).
Fiber sheath diameter: 60-500 µm (models FSM-100M and FSM-100P).
Fiber sheath diameter: 60-1200 µm (models FSM-100M+ and FSM-100P+).
Polarization-maintaining fiber splicing (models FSM-100P and FSM-100P+).
Fiber end analysis before splicing (models FSM-100M+ and FSM-100P+).
Advanced plasma zone control techniques (moving electrodes).
Operating temperature range: from 0°С to +40°С. Weight (depending on model): 7.5 - 9.0 kg.
High-quality welding of special fibers in the laboratory and in production
Need a welding machine for telecommunication networks? see model Fujikura 86S.
Want to see the full list? Go to main page fiber splicers.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The Japanese company Fujikura is famous for its machines for splicing classic single-mode and multimode optical fibers with a cladding diameter of 125 microns, which are used in data transmission networks. These are currently models Fujikura 86S and Fujikura 36S.
But besides telecommunications networks, optical fiber is widely used in other areas, such as laser systems, optical gyroscopes, sensors, various miniature devices, and many similar applications. Typically, the fibers used in all these applications differ from standard telecommunications fibers in two main ways.
First difference - this is the diameter, which, depending on the type of fiber, can vary from 60 to 1200 microns. At the same time, there are varieties, both with a round and non-round shape of the shell.
Second difference is the internal structure of the fiber. For different types of specialized fibers, it differs quite strongly. There are double sheath fibers. There are additional functional elements that are located parallel to the core (for example, in polarization-preserving fibers), etc.
For high-quality welding of such complex and diverse optical fibers in laboratory and production conditions, special welding machines with an extended set of functions are needed. Below on this page is a detailed description of the capabilities of the series of devices. FSM-100 Fujikura company. This series includes four professional models: FSM-100M, FSM-100M+, FSM-100P and FSM-100P+.
Double V-grooves
The FSM-100 Series utilizes a patented V-groove design that consists of two moving halves (referred to as Split v-groove in the figure below) to precisely center and securely hold fibers of varying sheath diameters. Together with the upper fiber clamps (called Clamp in the figure below), they form a three-piece fixing system that is able to hold fibers of different thicknesses in a precisely predetermined position.
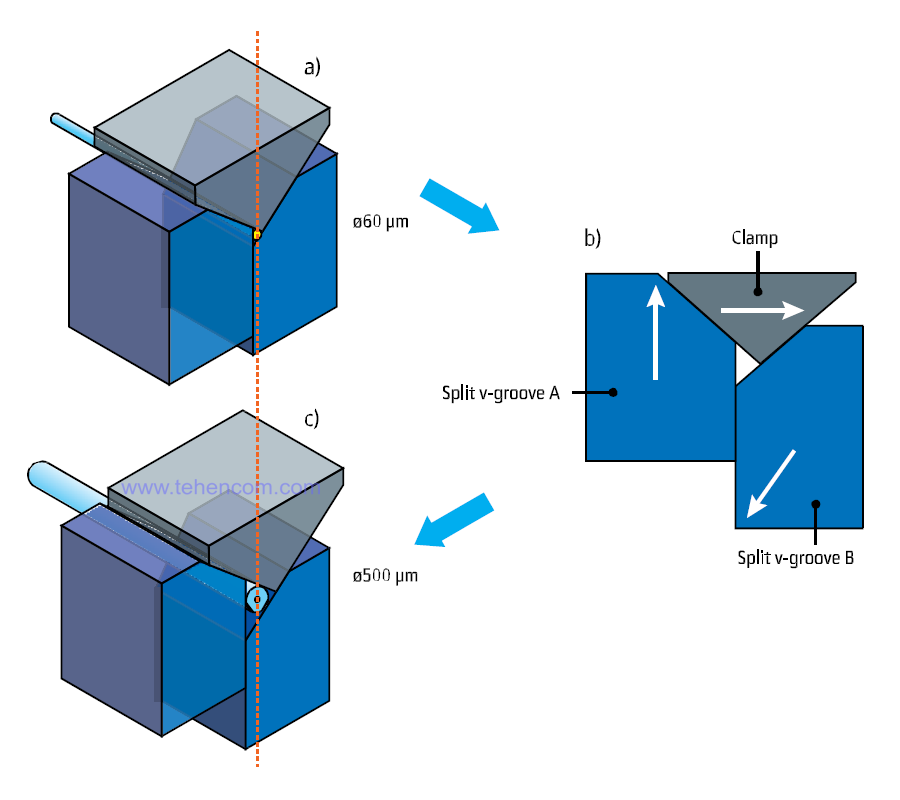
The appearance of this fiber fixation and centering system is shown in the photo below. This design of V-grooves provides the following advantages: reliable retention of fibers of different diameters, no need to replace or adjust the fixation system when changing the type of fibers, all the necessary parameters are already included in the software of the welding machine.
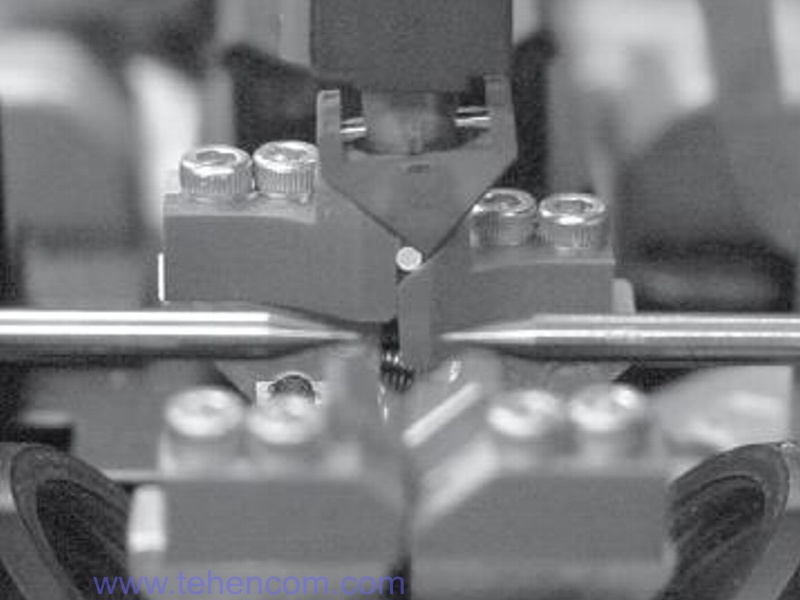

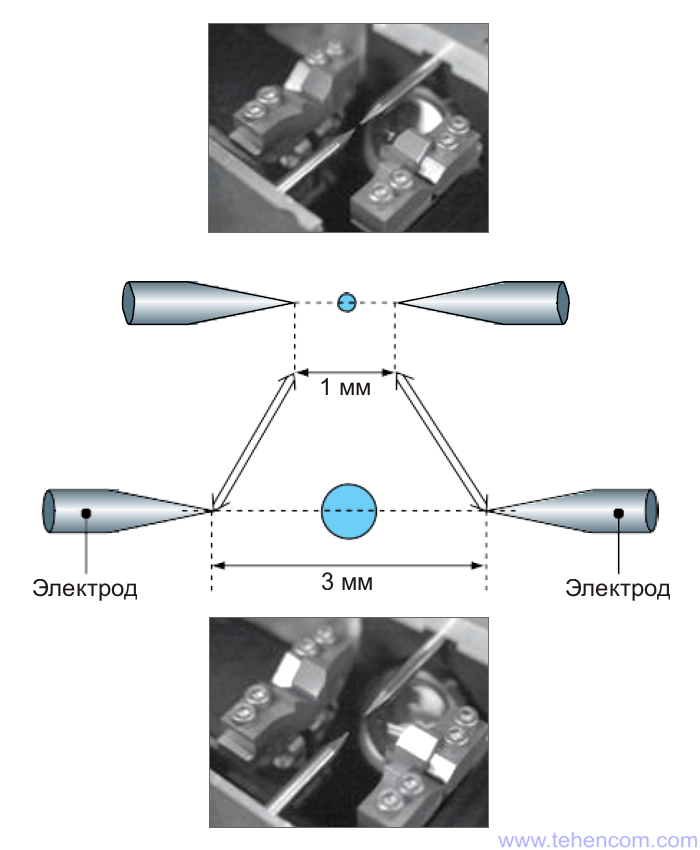
Flexible plasma zone control
In order to provide optimal welding conditions for fibers of different diameters, Fujikura FSM-100 series machines can flexibly adjust the parameters of the plasma zone that forms between the electrodes. This technology is called "Plasma Zone Fiber Positioning". For each device of the FSM-100 series, the distance between the ends of the electrodes can vary from 1 mm to 3 mm. An example is shown in this figure.
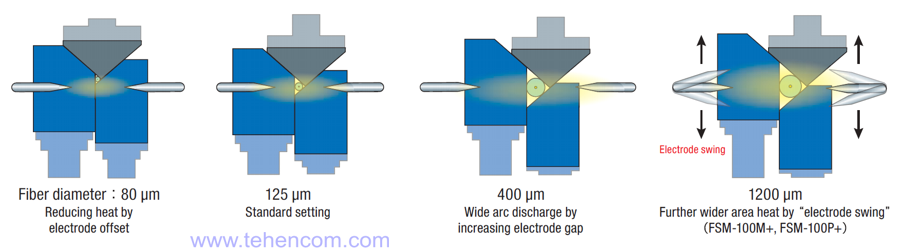
The second feature of the "Plasma Zone Fiber Positioning" technology is the ability to position the fiber splice point above, in the center or below the arc discharge. This allows high-quality welding of very thin fibers with a sheath diameter of less than 125 µm (in the figure below, this is the leftmost picture).
The second picture in the figure below illustrates the splicing of standard telecommunication fibers with a cladding diameter of 125 µm. In this case, the welding point is located in the center of the arc.
The third picture in the figure below illustrates the welding of thicker fibers with a cladding diameter of 400 µm. Please note that the welding point is also located in the center of the arc, but in this case the electrodes are separated by the maximum distance.
The fourth picture (far right) illustrates the splicing of fibers with a maximum cladding diameter of 1200 µm. Only two models of the FSM-100 series, namely FSM-100M+ and FSM-100P+, can work with such thick fibers. In these two models, the electrodes can be rotated around the attachment point, which provides extended control over the plasma zone. This additional technology, which is only available on models with a "+" sign, is called "Plasma Zone Path Modulation".
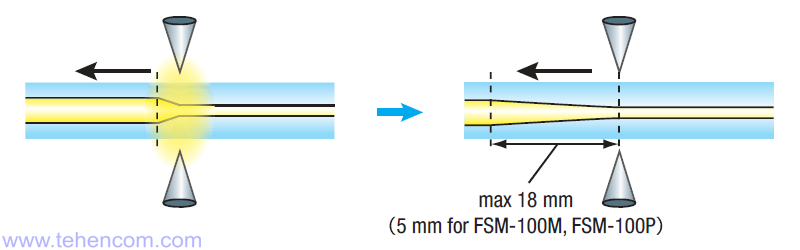
Possibility of pulling fibers during welding
The Fujikura FSM-100 series machines have the ability to move the fibers directly during the arc operation, which is used to implement various types of stretching of the welding zone. This function can reduce splicing losses of various types of optical fibers. In addition, it is used to treat non-round fibers just before splicing.
In the FSM-100M and FSM-100P, this feature is called "Sweep Arc Technology" and allows movement up to 5mm. And on the FSM-100M+ and FSM-100P+ models, this feature is called "Extended Sweep Arc Technology" and provides a greater distance of movement: up to 18 mm.
Fiber End Image Analysis
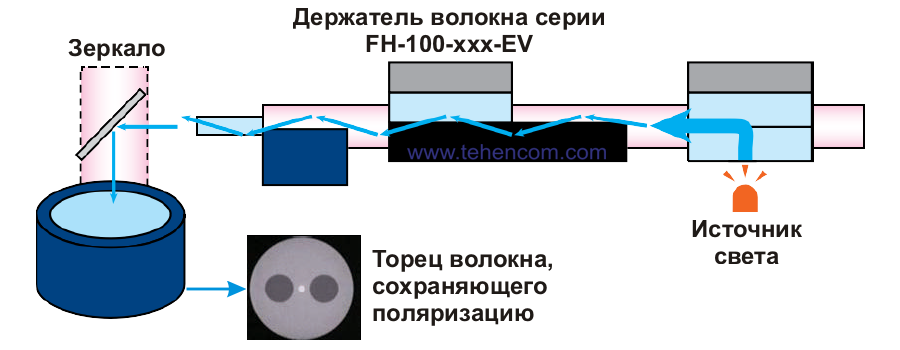
The Fujikura FSM-100M+ and Fujikura FSM-100P+ are equipped with an optional mirror system that can directly image fiber ends. To do this, light is introduced into it through the fiber cladding, which, passing through the fiber, exits through its chipped edge and enters through the mirror onto the camera of the welding machine. This feature is called "End View Alignment Technology". FH-100-xxx-EV series retainers must be used to hold the fibers.
Direct image analysis of the end faces provides additional opportunities for high-quality splicing of special types of fibers. For example, the Fujikura FSM-100P+ can use these images to mutually align and splice fibers while maintaining polarization. This figure shows schematically how the Fujikura FSM-100M+ and Fujikura FSM-100P+ imagers acquire fiber end faces.
Fusion splicing, maintaining polarization
Optical fibers, which maintain the polarization of the radiation passing through them, are widely used in industrial, military and scientific fields. Such fibers are called Polarization-Maintaining optical Fiber or PMF for short. New types of these fibers with increasingly complex core and sheath structures are being developed regularly. As an example, this figure shows a cross-section of some of the popular varieties of PMF fibers.
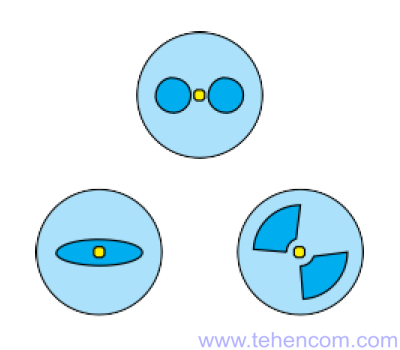
Precise alignment and high-quality welding of such fibers is a technically difficult task. In the Fujikura FSM-100 series, only two models can work with them, namely FSM-100P and FSM-100P+. PANDA fibers use the classic alignment method to work with them. by PAS technology. To work with any type of PMF fibers (both PANDA and non-PANDA), these devices use a new alignment method by IPA technology. In addition to these two methods, the FSM-100P+ can align the PMF of a fiber by analyzing its end-face images.
Precise alignment with rotation of optical fibers (IPA technology)
In order to qualitatively weld two fibers, while maintaining polarization, it is necessary that the apparatus can determine and accurately combine the structural elements of both fibers. At the same time, it is not enough to simply analyze the transverse brightness profile (as it is implemented in PAS technologies).
An advanced technology called Interrelation Profile Alignment, or IPA for short, uses fiber rotation around its axis in a fixed 20-degree increment. At the same time, more than ten key parameters of the transverse brightness profile are measured for each fiber position. This entire array of data is analyzed by the software of the device and the value of the angle of rotation is calculated, at which the internal structural elements of both fibers are aligned as accurately as possible.
This figure shows what data is measured and analyzed by the IPA algorithm for each angle of rotation of the optical fiber.
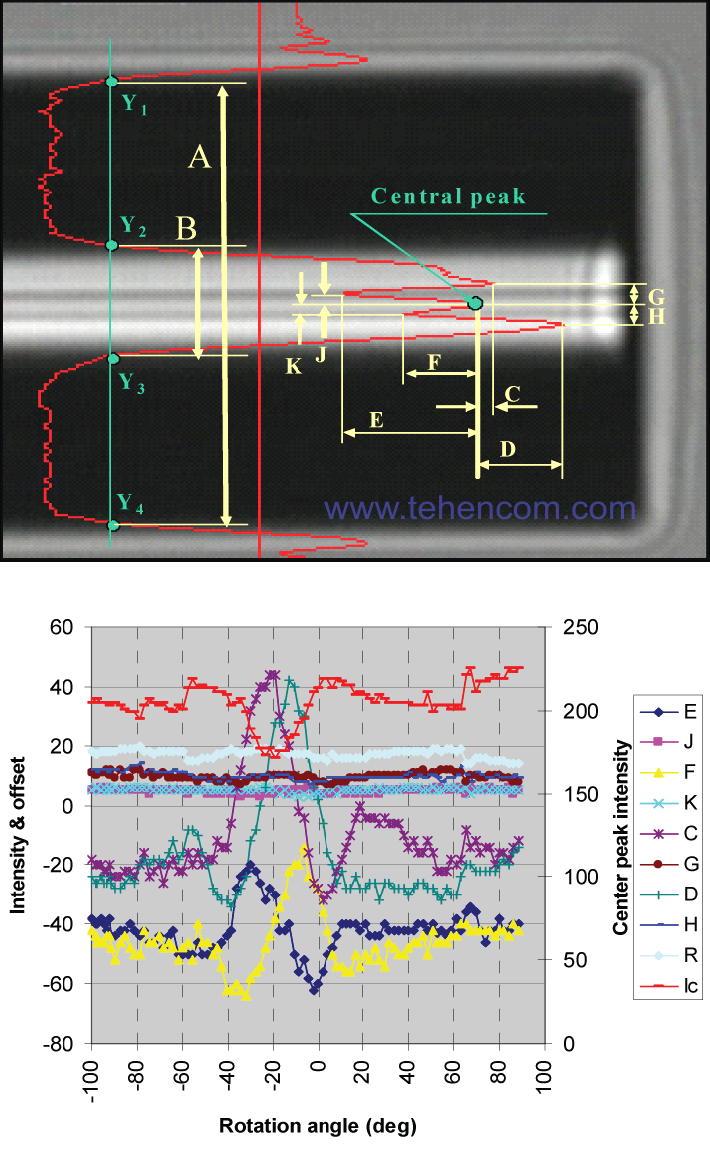
This careful analysis of an array of key parameters of the transverse brightness profile allows perfect fiber alignment, which ensures minimum splice loss for both known types of polarization-maintaining fibers and new ones that will appear in the future.
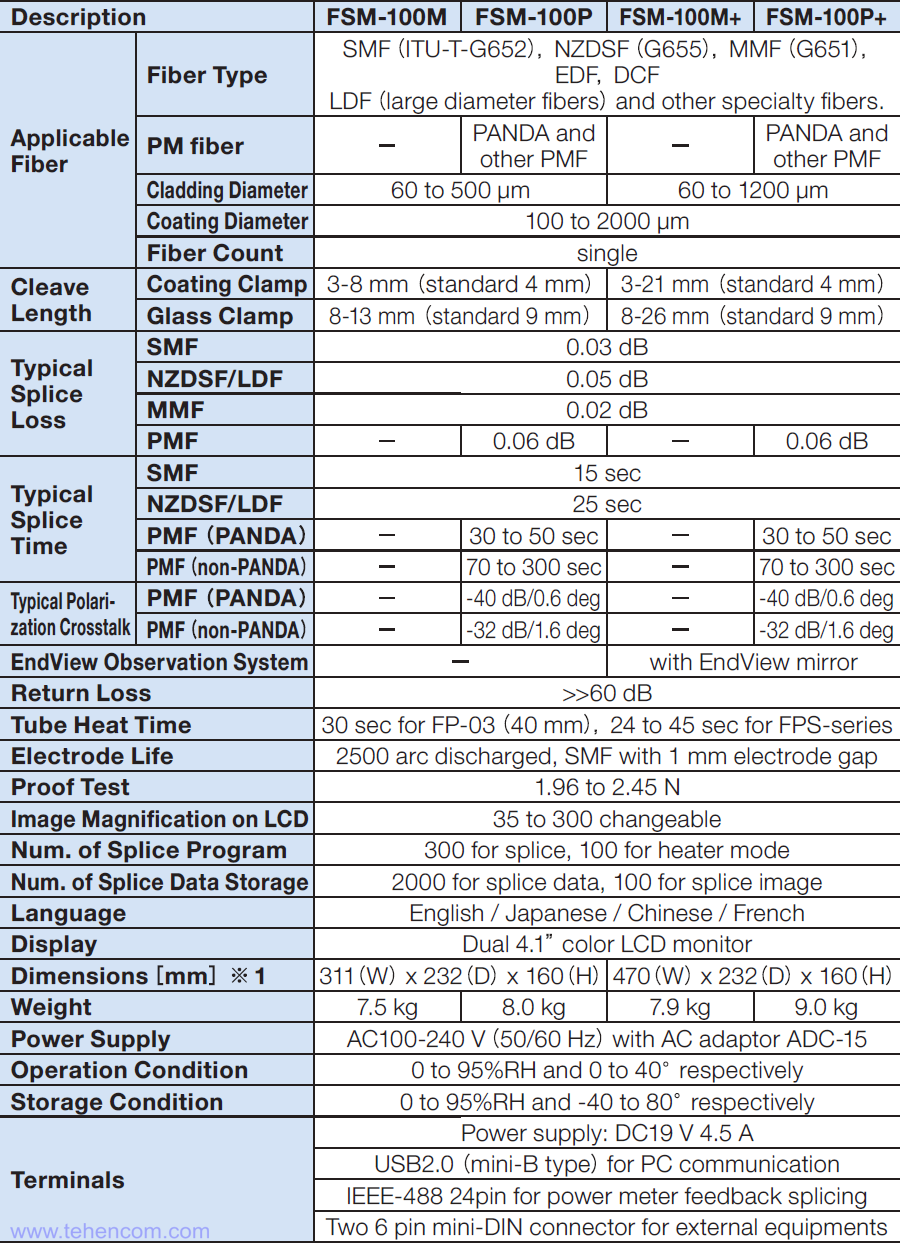
Specifications of Fujikura FSM-100 Fiber Splicer
Here is a list of the main features of the Fujikura FSM-100 series fiber splicer. For detailed technical specifications, see below on this page in the section Documentation.
Documentation
This PDF documentation contains the most comprehensive description of the Fujikura FSM-100 series fiber splicer features, specifications and operating modes.
Description and characteristics of Fujikura FSM-100 welding machines (in English) (4 pages; 3 MB)
Fujikura Specialized Welding Machine Brochure (English) (8 pages; 3 MB)
Fujikura Service Center Certificate (1 page; 1 MB)
And here you can find our tips and other useful information on this topic:
Types of devices according to the method of alignment (alignment) of optical fibers
Effect of electrode wear on welding quality, electrode replacement procedure
How to buy equipment cheaper - discounts, special prices, demo and used devices
To simplify the process of choosing a splicer for fiber optics, you can use our experience and recommendations. We have over 20 years of practical supply experience and can immediately answer many questions about models, options, delivery times, prices and discounts. This will save your time and money. For this it's simple call us or write to us at Email and we will be happy to answer your questions.